Many innovative schools and districts are integrating employability skill development into K-12 instruction, assessments, and work-based learning initiatives. This approach nurtures well-rounded graduates who are prepared to excel in college, their careers, and life.
Equally important, this focus meets the needs of future employers. A study by BNG found that 84% of employees and managers consider soft skills essential for new hires, with 90% of larger companies ranking them as a top priority. These skills are critical for hiring decisions, career growth, and standing out in a competitive job market.
Read on to explore what employability skills are, why teaching them matters, and actionable next steps to implement effective frameworks districtwide.
What Are Employability Skills?
Employability skills are the essential tools needed to succeed in any job. These skills encompass both technical abilities and soft skills, such as interpersonal and personal attributes. Hard skills—like coding or accounting software—are often gained through education or training. Soft skills—such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving—are qualities that influence how well someone works with others.
A strong set of employability skills turns students into great candidates. More importantly, it equips them to acquire new skills later in life.
10 Employability Skills That Will Matter Most in 2025
The modern workplace demands technical know-how, but true success comes from developing essential life skills. To help students thrive in any career, here are ten key competencies to focus on:
Technical Skills
- Digital Fluency: Equips students with a strong understanding of technologies like AI, automation, and cloud platforms, which are becoming staples in today’s workplace.
- Data Literacy: Helps students build the knowledge and skills to interpret, analyze, and apply insights from data, while also equipping them to effectively use data analysis tools.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Introduces students to the basics of recognizing and mitigating cyber threats, protecting sensitive information, and understanding how to respond to potential risks. This foundational knowledge helps students navigate modern digital environments safely and responsibly.
- Design Thinking: Prepares students to tackle problems with creativity and a focus on practical solutions. By considering user needs and testing ideas, they learn to address challenges in ways that are both innovative and effective—a valuable skill for any role involving collaboration, problem-solving, or process improvement.
- Media and Information Literacy: Enables students to evaluate the credibility of information by analyzing sources and distinguishing facts from misinformation. This skill is crucial for roles involving research, critical thinking, and informed decision-making.
- Digital Collaboration Tools: Helps students collaborate effectively in teams, whether in person or remotely. Proficiency with tools like video conferencing, shared documents, and project management platforms ensures smoother communication and teamwork.
Life Skills
- Growth Mindset: Students with a growth mindset believe their abilities can improve with effort. This perspective encourages them to work harder, face challenges, and see setbacks as opportunities to grow.
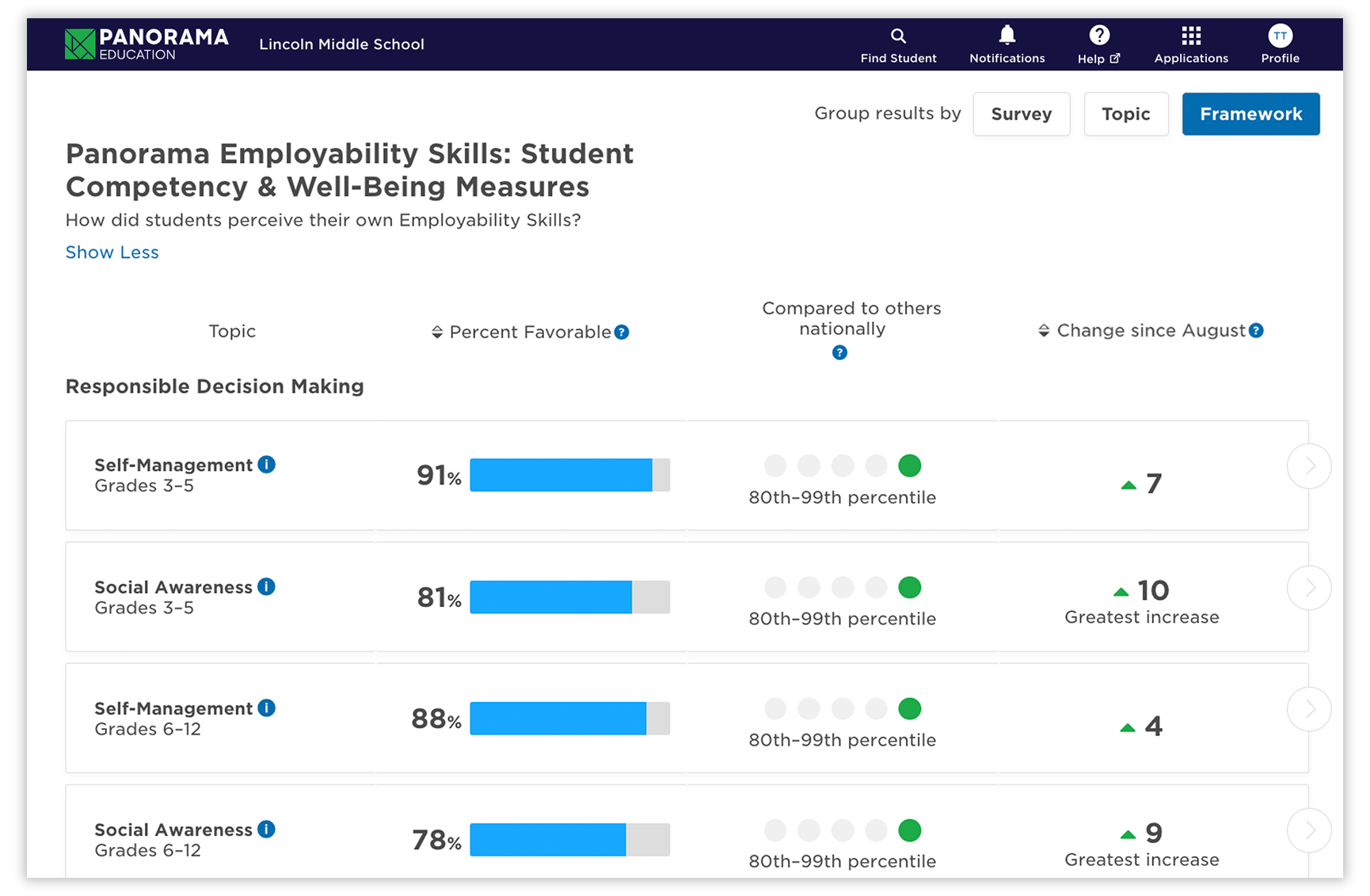
- Self-Management: Self-management involves managing emotions, time, and responsibilities effectively. Skills like goal setting, preparation, and focus are key to success in college, work, and life.
- Social Awareness: Social awareness helps students understand and empathize with others’ perspectives. This skill enables them to work well in teams, resolve disagreements calmly, and build stronger relationships.
- Self-Efficacy: Self-efficacy is the belief in one’s ability to succeed. Students with this confidence are more likely to set ambitious goals, take on leadership roles, and connect effort to achievement.
- Emotion Regulation: Emotion regulation equips students to manage feelings like anger, frustration, and anxiety. It helps them cope with challenges, adapt to change, and build resilience in new situations.
- Social Perspective-Taking: This skill teaches students to understand others’ thoughts and feelings, including those of adults and peers. It encourages empathy, helping them navigate diverse perspectives and experiences.
How to Develop Employability Skills in Students
Without employability skills, students may face challenges early in their careers, lacking a clear understanding of workplace expectations. These skills are essential for success in college, careers, and life beyond. Here’s how to help students develop them:
-
Project-Based Learning
Use real-world projects to teach problem-solving and teamwork. Assign tasks like creating prototypes, solving community problems, or designing marketing plans to help students learn collaboration and practical thinking. This project-based learning approach helps students learn how to collaborate, think critically, and apply their knowledge.
-
Internships and Work Experience
Provide hands-on experience through internships and work placements. Partner with local businesses to offer mentorship, workshops, and insight into workplace expectations. These opportunities help students understand professional environments, build practical skills, and explore potential career paths before they graduate.
-
Career Guidance Programs
Offer career counseling to help students identify strengths, set goals, and understand job market trends. Provide job market insights, including in-demand skills and industries, to prepare them for their futures.
-
Resume and Interview Preparation
Hold resume workshops, and run mock interview sessions to teach students how to answer questions, present themselves confidently, and understand employer expectations.
-
Digital Literacy
Incorporate technology into lessons to teach essential digital tools and platforms students will use at work. Teach students how to use collaboration platforms, data analysis tools, and other workplace technologies to prepare them for modern job requirements.
-
Extracurricular Activities
Organize clubs, leadership roles, and activities like student councils, sports teams, or community projects to help students develop teamwork, problem-solving, and decision-making skills outside the classroom.
-
Public Speaking Practice
Provide opportunities for presentations, debates, and speaking exercises to help students communicate clearly and these experiences teach them how to articulate ideas clearly, engage an audience, and perform under pressure.
Employability Skills and CTE Pathways
Career and Technical Education (CTE) is a powerful pathway for equipping students with the employability skills they need to succeed in today’s workforce. By combining academic instruction with hands-on, real-world experiences, CTE programs help students develop both technical expertise and soft skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. Whether it’s through learning how to troubleshoot mechanical systems in a manufacturing class or practicing customer service in a hospitality course, CTE allows students to build the confidence and competencies they’ll need to thrive in their chosen fields. These programs often align with industry standards, ensuring students graduate with skills that are immediately relevant to employers.
In addition to technical training, CTE pathways place a strong emphasis on employability skills by fostering critical thinking, adaptability, and collaboration. For example, students may engage in project-based learning, where they tackle challenges similar to those faced in the workplace. They also gain experience with tools and technologies commonly used in their industries, such as data analysis software or project management platforms.
This dual focus not only prepares students to enter the workforce but also equips them with lifelong skills that enable them to adapt to new roles, industries, and challenges as their careers evolve. By integrating CTE into K-12 education, districts can ensure students graduate ready for both the demands of their first jobs and the opportunities of the future.
Gauge Students' Employability Skills with Panorama
As districts plan for the next academic year, it’s essential to take a proactive, system-wide approach to employability. That means building foundational skills in elementary and middle school while supporting high schoolers through graduation and post-secondary pathways. With CTE programs and career prep top of mind, educators need the right tools to ensure students are developing the competencies needed for life after school—before it’s too late.
Panorama Student Success equips districts to build employability skills by connecting the dots across academics, attendance, behavior, and life skills. As a leading MTSS platform, it helps educators understand the whole child, identify students in need of support, and deliver interventions that build the habits and mindsets essential for future success. Early warning indicators help ensure students stay on track—and no one falls through the cracks.
.png?width=1728&height=1132&name=student%20overview%20life%20skills%20(3).png)
Panorama Student Success (demo data displayed)
Insights from Panorama Surveys and Engagement elevate student and community voice, shaping employability efforts that reflect both student aspirations and local workforce needs. By gathering feedback on school climate, learning experiences, and post-secondary goals, districts can align career pathways with what students need to succeed—and what their communities need to thrive. This leads to more meaningful, relevant opportunities that connect learning to real-world careers.
Together, Student Success and Panorama Surveys provide a holistic system to support students in their next step—whether entering a career, technical training, or further education.