In districts nationwide, educators face the challenge of equipping students with skills that extend beyond textbooks and exams. These skills are crucial to academic—and life—success.
And building these skills is now more important than ever. We’ve recently uncovered significant and ongoing shifts in students’ learning experience since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Our findings underline the need for strong systems of support for students to continue to build important skills—including key learning skills, educational environments, and relationships they need to face future challenges.
What Are Life Skills?
Schools and districts often refer to life skills using a range of terms, including: resiliency skills, durable skills, character skills, 21st century skills, employability skills, workforce skills, and college & career readiness skills.
Regardless of the term used, it’s crucial that students build these skills for success across academics and life. Given the diverse nature of life skill instruction, we’re focusing on five life skills for k-12 educators to nurture in students:
- Growth Mindset
- Emotion Regulation
- Self-Efficacy
- Self-Management
- Social Awareness.
These skills not only help educators shape academically proficient individuals, but also foster a generation prepared for success in the classroom and in an ever-changing world.
Life Skill 1: Growth Mindset
A growth mindset is not just an attitude; it's a powerful perspective that shapes student perceptions of their potential to influence crucial factors in their academic performance. This mindset fosters a belief that with dedication, hard work, and perseverance, intelligence, and abilities can evolve and improve over time. It involves a conviction that talents are not fixed but can be nurtured.
As children embrace the belief that effort leads to improvement, they discover a willingness to take on challenges, solve problems, and learn from setbacks. This mindset not only fuels a love for learning, but also equips students with a mindset essential for navigating the complexities they’ll encounter throughout life.
Practical Strategies for Promoting Growth Mindset in Educational Settings
To cultivate a growth mindset in students, educators can consider practical classroom strategies, which are critical in shaping a growth-focused learning environment:
- Encourage a culture that values effort and progress alongside achievement
- Provide constructive feedback that emphasizes process rather than only outcome
- Integrate challenging tasks that stretch students beyond their comfort zones, fostering a sense of resilience and determination
- Inspire self-reflection, helping students recognize and celebrate their own growth
By incorporating these strategies, educators can nurture a mindset that propels students toward a future where they confidently embrace challenges, persist through difficulties, and view learning as a lifelong journey.
Read the Success Story: How Cielo Vista Elementary Created an 8% Increase in Students’ Growth Mindset
Life Skill 2: Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation is a cornerstone for student well-being. It encompasses the ability to effectively manage and navigate one's emotions. More than just feeling their emotions, children must learn how to handle and express them appropriately.
Emotion regulation plays a pivotal role in a student's ability to navigate the complexities of both academic and personal spheres, extending the importance of this skill far beyond the classroom. Learning emotion regulation empowers students to:
- Face stressors and challenges with composure
- Communicate interpersonally with clarity and confidence
- Take ownership of their overall mental health and well-being
- Make sound decisions
- Cultivate positive relationships
Techniques for Teaching Students to Regulate Emotions
Teaching students how to regulate their emotions involves providing them with a toolkit of practical techniques, including:
- Fostering self-awareness, helping students recognize and understand their emotions
- Encouraging mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing or meditation, to promote emotional balance
- Developing strategies for constructive expression, guiding students on effective communication when navigating strong emotions
- Equipping learners with problem-solving skills to address the root causes of emotional challenges
Teachers should also consider intervention strategies like the 2x10 Relationship Building Strategy. This Tier 2 intervention supports children who might have trouble regulating themselves by reinforcing positive behaviors and conveying genuine support to foster stronger teacher-student relationships. Research shows that implementing this intervention can contribute to significant improvements in individual student behavior and the classroom environment at large.
By incorporating these emotion-regulating techniques, educators lay the foundation for students to navigate a spectrum of emotions with resilience and self-assurance.
Life Skill 3: Self-Efficacy
A crucial factor in a student's journey, self-efficacy signifies a student’s personal belief in their ability to accomplish specific tasks and achieve academic success. Beyond mere confidence, this life skill requires a deep understanding that one's efforts directly influence the outcomes they seek. In essence, self-efficacy embodies the conviction that challenges are conquerable, making learning an attainable journey.
The extent to which students believe in their ability to achieve their goals directly influences their motivation, resilience, and overall approach to learning. A high level of self-efficacy nurtures a mindset where setbacks become opportunities to learn and grow, propelling students toward continuous improvement.
Activities & Methods to Enhance Self-Efficacy in Students
To help boost self-efficacy in students, educators should consider implementing intentional activities and methods:
- Cultivate a supportive environment that recognizes and celebrates individual achievements, reinforcing the idea that effort leads to success
- Encourage goal-setting, breaking down larger objectives into manageable steps to instill a sense of accomplishment
- Offer constructive feedback that spotlights strengths and areas for improvement, guiding students toward a realistic assessment of their capabilities
- Instill a growth mindset, emphasizing the potential for improvement through dedication and perseverance
By integrating these activities, educators empower students not only to believe in their capabilities, but also to actively shape their academic journey with confidence and purpose.
Life Skill 4: Self-Management
Students equipped with self-management skills can navigate the complexities of academic and personal challenges. They approach tasks with finesse, demonstrating adept control over their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Students with strong self-management skills adapt to various situations, fostering autonomy and mastery over their actions.
Beyond mere self-control, self-management empowers students to understand and adapt to a variety of situations, cultivating ownership and mastery of their actions. This capability becomes a guiding force, enabling students to navigate the complex interplay of their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors across diverse situations.
Tips for Helping Students Improve Self-Management Skills
To support the development of this life skill, educators must empower students to respond thoughtfully and purposefully to the challenges they encounter. Educators can incorporate the following strategies into the classroom environment to do so:
- Encourage Reflection: Prompt students to reflect on their emotions, thoughts, and reactions in various situations. This self-awareness forms the foundation for effective self-management.
- Set Clear Objectives: Guide students in setting clear objectives and actionable steps. Goal-setting helps them break down tasks into manageable parts, fostering a sense of accomplishment.
- Teach Time Management: Instill effective time-management strategies to help students allocate their resources wisely. This skill ensures they can balance academic and personal responsibilities.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Offer constructive feedback that emphasizes strengths and areas for improvement. This helps students realistically assess their capabilities, contributing to a positive self-perception.
- Promote Resilience: Emphasize the importance of bouncing back from setbacks. Resilience is a key component of self-management, teaching students to navigate challenges with grace and perseverance.
Life Skill 5: Social Awareness
Equipped with the ability to empathize and consider diverse perspectives, children with social awareness skills are architects of a better world. As they grow, they contribute to harmonious communities, breaking down barriers and paving the way for a more interconnected and compassionate world. By helping students develop social awareness skills, educators contribute to the development of students who not only excel academically, but also possess the tools needed to thrive in diverse and interconnected communities.
Strategies for Fostering Social Awareness
By prioritizing empathy and encouraging various viewpoints, educators empower students to become not just academically proficient individuals but also compassionate, understanding citizens. Fostering social awareness within the classroom requires intentional strategies:
- Cultivate an Inclusive Environment: Create a classroom culture that encourages open dialogue. This sets the stage for students to appreciate and learn from each other's unique perspectives.
- Incorporate Various Perspectives: Integrate different voices and perspectives into the curriculum. This exposure broadens students' worldviews, enhancing their ability to understand and connect with others.
- Encourage Empathy Exercises: Introduce empathy-building exercises and activities that prompt students to step into the shoes of their peers, nurturing a genuine understanding of others' feelings and experiences.
- Promote Collaborative Projects: Design collaborative projects that require students to work together, fostering teamwork and mutual understanding. Real-world collaboration prepares students for future endeavors that require social acumen.
Next Steps for School and District Leaders
Life skills empower students to become resilient, adaptable individuals. These tools are a critical component of 21st century skills, and an important aspect of supporting college-career readiness. Empowering educators to weave these skills into the fabric of daily learning environments is an investment in a future where students not only excel academically, but also emerge as empathetic, socially-aware contributors to society.
Measuring and assessing life skills to best support students’ comprehensive growth can be challenging. Panorama’s Life Skills Surveys and School Climate Surveys are powerful tools for aligning district focus areas and promoting a comprehensive educational experience.
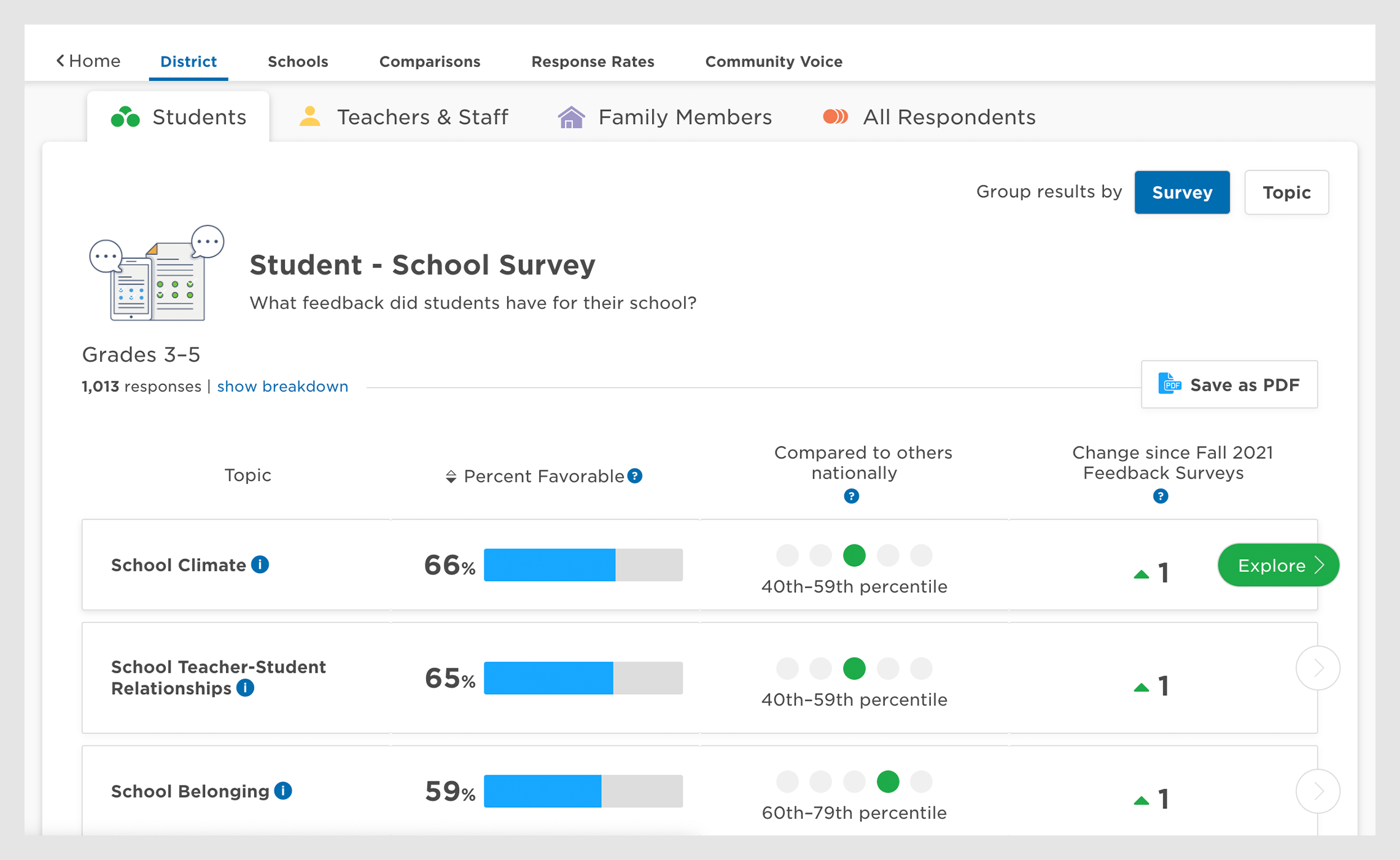
Panorama's Student Survey (demo data pictured)
By focusing on these skills and implementing programs that assess and support their cultivation in students, district leaders and educators not only prepare students for the future, but help them to become well-rounded, resilient, and confident leaders of tomorrow.






